Product > Evaporators > Agitated Thin Film Evaporator
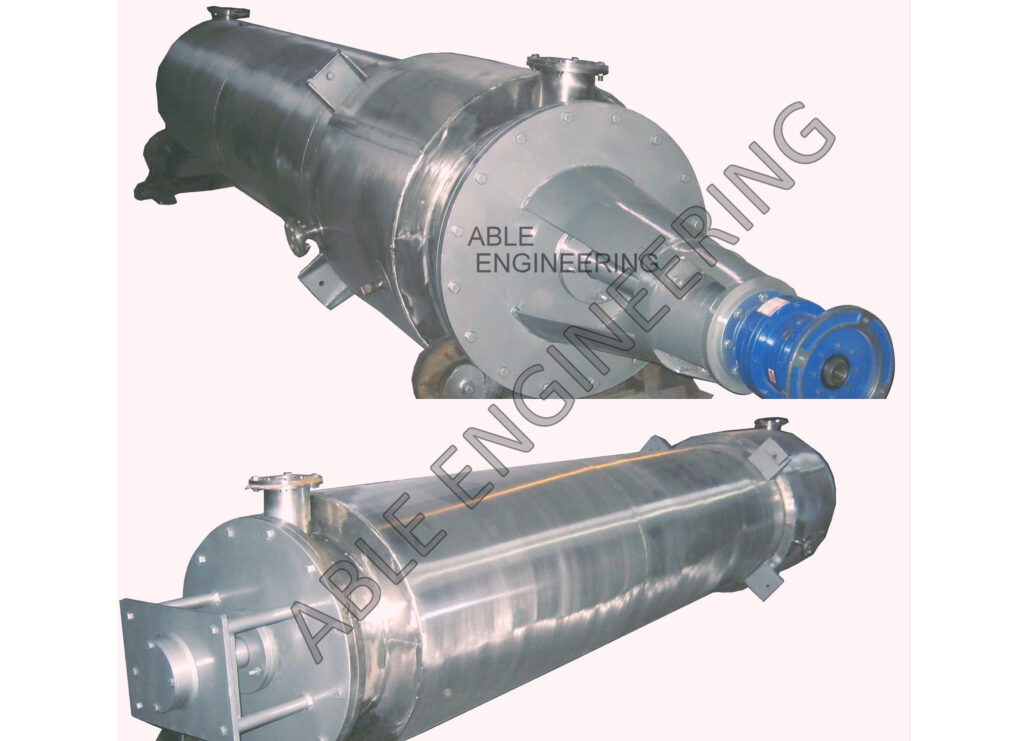
Agitated Thin Film Evaporator
Agitated Thin Film Evaporator is well-known among buyers for its high-quality features and is best suited for heat-sensitive products where drying time and temperature are critical. Our agitated thin film evaporator is for drying, vacuum distilling, and many more uses. We are counted as one of the leading manufacturers and exporters of Agitated Thin Film Evaporators.
Able Engineering‘s agitated thin film evaporators quickly separate volatile from less volatile components using indirect heat transfer and mechanical agitation of a flowing product film under controlled conditions. Either the vaporised component (distillate) or the concentrated component may be the product. Able Engineering provides turnkey solutions for Herbal Extraction Plants, Phytoextraction Plants, and Phytochemical Plants.
How Thin Film Evaporator Works:
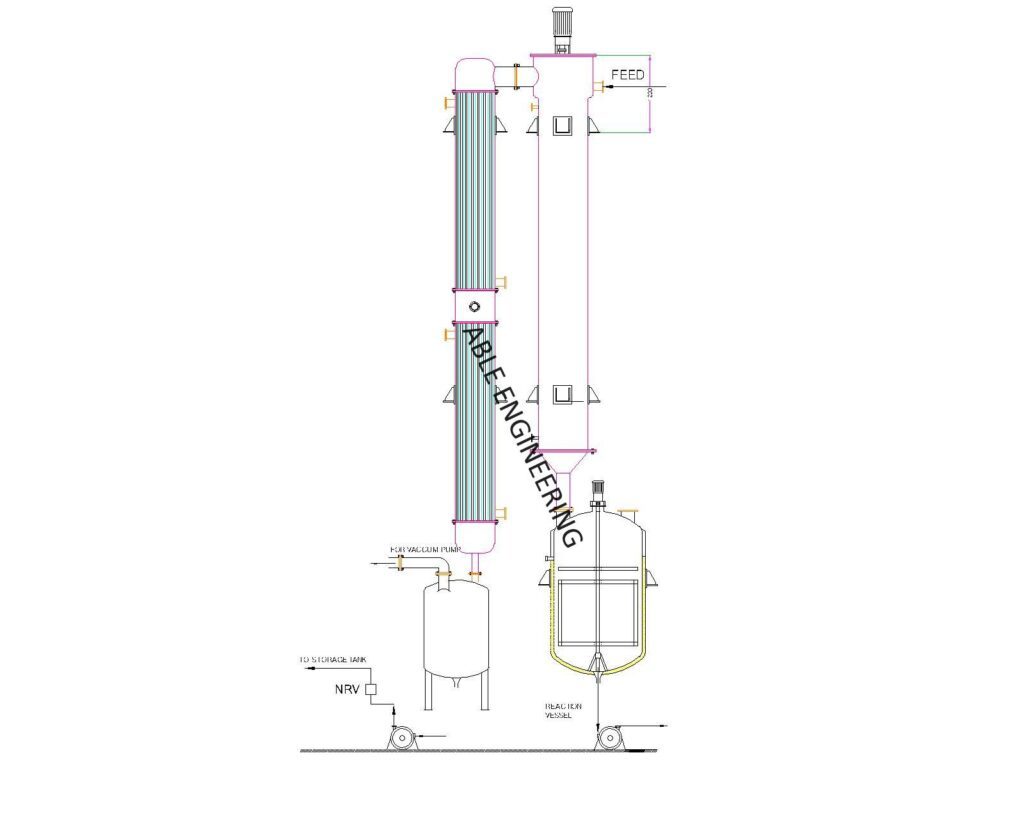
The product is continuously fed into the thin film evaporator above the heating jacket and spread onto the periphery of the distribution ring. The product was then picked up by the rotor blades and immediately formed into a thin turbulent film on the heat transfer surface. The volatile components of the feedstock very quickly evaporated and flowed counter-currently with reference to the feed, up towards the top of the evaporator and into the rotating separator. Here, entrained droplets or foam are knocked out of the vapour stream and return to the evaporation zone. The evaporated components then flow out of the evaporator into the condensation stage, column, or another downstream process step.
For special applications, co-current vapor/product flow is used, in which a separation vessel is fitted at the bottom of the evaporator below the rotor in place of the normal rotor-mounted separator and the upper vapour outlet nozzle.
Thin Film Evaporator Advantages :
- Suitable to high vacuum distillation with very low residence time.
- Narrow spread.
- Avoid product re-circulation and possible degradation.
- Apt for viscous products.
- Ideal for hazardous applications.
Thin Film Evaporator Applications :
- Vacuum Distillation.
- Drying.
- Solvent Recovery.
- The Concentration of bulk drugs, enzymes, juice, milk product etc.

About Us
Able Engineers Private Limited, also known as Able Engineering, is a Fabrication company that offers our clients a wide breadth of experience and knowledge. Our team of professionals has vast experience in the Herbal Extraction Plants & Herbal and Solvent Extraction Plant Machinery, Pharmaceutical Plant Machinery, Food Processing Plant & Food Processing Plant Machinery, and Chemical Plant Machinery & Calcium Machinery plants. We are able to satisfy the needs of a wide range of clients. Having been involved in projects covering a broad range of industrial sectors, including reactors, rotary extractors, and other pharmaceutical machinery, we have the flexibility to tailor our production to meet the needs of our clients.
Our experience and expertise also allow us to work closely with our clients from the design stages until final dispatch. This combination of steel fabrication, rolling, forming, and welding, together with a working practical knowledge of the industries served, allows us to provide a full and comprehensive service with the aim of complete customer satisfaction.
Our every employee believes value engineering is an important part of our work, and we provide solutions, not just products. Our teams of qualified, experienced engineers and technicians can create and build to client specifications, whatever the challenge. The clients have ensured the highest levels of product quality and workmanship, including on-time completion. Our mission is to provide high-quality service/ product combined with trusted client partnership and to maintain high health and safety levels and solutions to the client’s needs.
Our Values
- Quality and safety first.
- Monitoring continuous improvement through learning and development.
- Innovation and creativity in solving problems.
- An empowered, committed, and motivated workforce.
